Basic CI Pipeline
The pipeline described here will be triggered after a developer has promoted their code in ISPW from DEV to QA within an ISPW application. The container resulting from the promote, and subsequent triggering of this pipeline, will be the ISPW set generated by the promote. The pipeline will implement the general process steps.
Setting up the pipeline job
The pipeline job itself is defined within Jenkins by creating a new pipeline job. It is important, to make sure that the resulting job uses parameters by checking the `This project is parameterized' box.
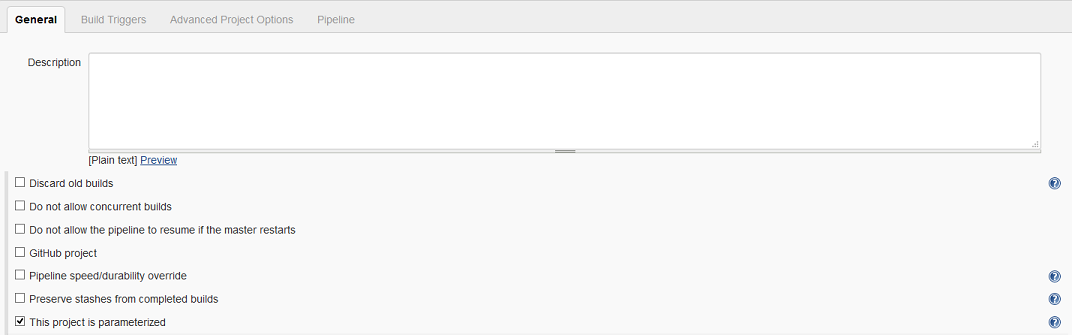
The pipeline parameters
Successively add the following string parameters (default values are used in the examples).
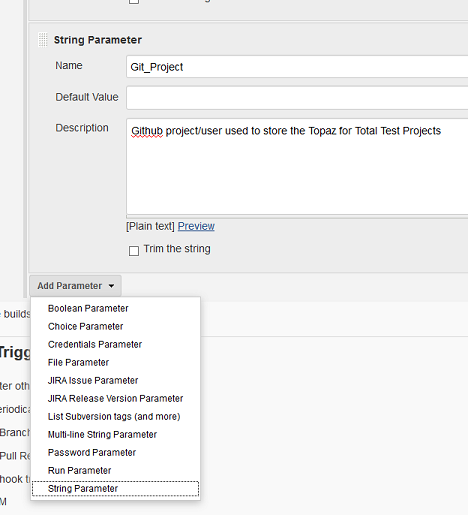
The parameters in this first set are specific to the individual execution of the pipeline and get passed by the ISPW Webhook
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
ISPW_Stream | ISPW Stream Name |
ISPW_Application | ISPW Application |
ISPW_Release | ISPW Release Name |
ISPW_Assignment | ISPW Assignment |
ISPW_Src_Level | ISPW Level the promote has been started from |
ISPW_Owner | ISPW Owner User ID |
The second set of parameters are installation specific settings, reference tokens, and other IDs that have been defined during the configuration phase in Jenkins. They allow setting up different jobs, using different values for the configuration settings (if required) but using the same script for execution. To determine the appropriate values to use, refer to the description of the pipeline parameters.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CES_Token | CES Token, will be required by the XL Release Template |
Jenkins_CES_Token | Jenkins credentials ID storing the CES Token, will be used for ISPW operations |
HCI_Conn_ID | Jenkins internal ID for HCI Connection |
HCI_Token | Jenkins credentials ID TSO logon to HCI |
CC_repository | Code Coverage Repository - Check with your Xpediter Code Coverage administrator for the name to use |
Git_Project | Github (or other Git based repository) project used to store the Topaz for Total Test Projects |
Git_Credentials | Jenkins credentials ID for logon to Git server |
Loading the script from GitHub
Instead of using a Pipeline script and placing the pipeline code into the Script text box, the pipeline uses a Pipeline from SCM stored in GitHub. Make sure to use the proper GitHub (or other Git server version) branch, path, and file name to point to the script file. The example uses the master branch and file src\Jenkinsfile\Mainframe-CI-Example-pipeline.jenkinsfile.
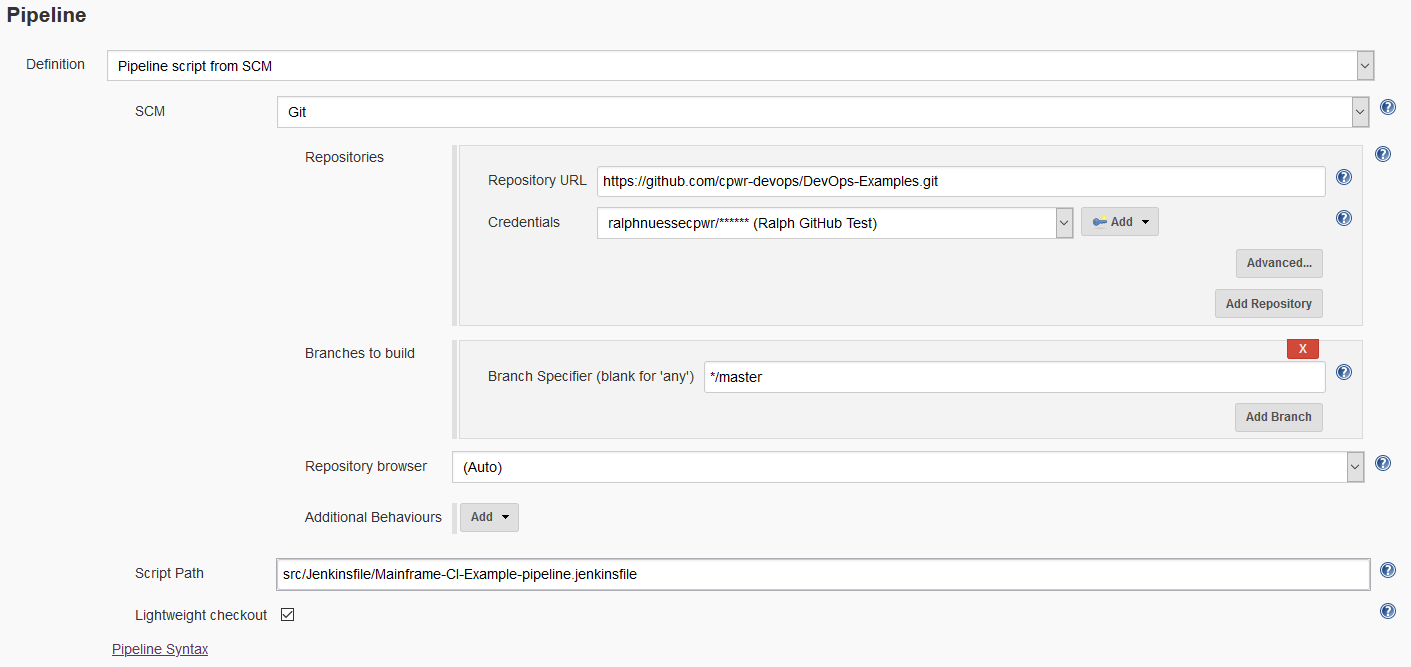
Jenkins Pipeline Script
Once this pipeline has been triggered, the pipeline will execute the following code implementing the previously described steps.
Global Variables
The first part initializes global variables that are specific to the environment the pipeline executes in and will neither differ between executiuons of any given job, nor between different jobs using the same script.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Git_URL | URL to the GitHub project containing the repository storing the TTT projects |
Git_TTT_Repo | Name of the repository |
Git_Branch | GitHub branch to use for accessing the TTT scenarios |
SQ_Scanner_Name | Name of the Sonar Scanner as defined in Jenkins Manage Jenkins->Global Tools Configuration->SonarQube Scanner |
SQ_Server_Name | Name of the SonarQube server configuration in Jenkins Manage Jenkins->Configure System->SonarQube servers |
SQ_Project | Name of the SonarQube project to use |
MF_Source | Folder that the ISPW download plugin will download the sources to |
XLR_Template | Name of the XLRelease release template to use when triggering the releas |
XLR_User | Jenkins credentials token to use to connect to XLRelease |
TTT_Folder | The code will download the TTT projects to this sub folder of the Jenkins workspace |
TTT_Vt_Environment | ID of environment defined in the Topaz for Total Test repository to be used for execution of tests |
TTT_Sonar_Results_File | Name of the SonarQube results file generated by the Topaz for Total Test CLI |
CES_Url | URL for CES |
ISPW_Runtime | ISPW runtime configuration to use |
ISPW_Changed_Programs_File | Name for the .json file created by ISPW for Intelligent Test Case Execution |
mailRecipientMap | Groovy Map (opens new window) to store ISPW Owner Ids (TSO user id) and email addresses |
String Git_URL = "https://github.com/${Git_Project}"
String Git_Ttt_Repo = "${ISPW_Stream}_${ISPW_Application}_Total_Tests.git"
String Git_Branch = "master"
String SQ_Scanner_Name = "scanner"
String SQ_Server_Name = "localhost"
String SQ_Project = "${JOB_NAME}"
String MF_Source = "MF_Source"
String XLR_Template = "A Release from Jenkins"
String XLR_User = "admin"
String TTT_Base_Folder = "Tests"
String TTT_Vt_Folder = "Virtualized_Tests"
String TTT_Vt_Environment = '123456789123456789123456'
String TTT_Sonar_Results_File = './TTTSonar/generated.cli.suite.sonar.xml'
String CES_Url = "http://ces.server:2020"
String ISPW_Runtime = "ispw"
String ISPW_Changed_Programs_File = 'changedPrograms.json'
Map mailRecipientMap = ["ABC1234":"name@company.com"]
Node and Stages
The node statement tells Jenkins which node (agents in a Jenkins network) to use. It may be used to distribute work, run jobs in parallel, or run steps in a job in parallel. This pipeline will use one node with several stages. All variables defined within the node are local to the node and available to all stages therein.
node{
Initialization
The example application uses three parallel paths (DEV1, DEV2, DEV3). In order to use the correct STEPLIB concatenation in the Topaz for Total Test runner.jcl there are three versions of the JCL file in each Topaz for Total Test project used. To determine the correct JCL file to use, the script determines the current path from the ISPW level being passed to the pipeline. Using the path number, the name for the runner JCL to be used is being built and the next level in the path being determined.
def PathNum = ISPW_Src_Level.charAt(ISPW_Src_Level.length() - 1)
def ISPW_Target_Level = "QA" + PathNum
def CC_DDIO_Override = "SALESSUP.${ISPW_Application}.${ISPW_Target_Level}.LOAD.SSD"
Get the email address of the owner of the promotion set from the map of mail recipients.
def mailRecipient = mailRecipientMap[(ISPW_Owner.toUpperCase())]
Stage # - Clear out the workspace
This stage cleans out the workspace from any previous runs of the pipeline. The call to dir(...) sets the location to the root of the workspace. Any code within the code block is executed in relation to this location. Therefore, the deleteDir() will delete the current directory including all sub folders.
stage("clean previously downloaded source")
{
dir("./")
{
deleteDir()
}
}
Stage # - Download sources from ISPW
This stage downloads all COBOL sources and COBOL copybooks from ISPW (the mainframe) that are part of the set triggering this specific pipeline execution, using the ISPW Container downloader. The code has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": Checkout, "SCM": ISPW Container.
Note 1
The containerType parameter tells the plugin which type container is passed via the containerName parameter. Valid values are
- 0 - Assignment
- 1 - Release
- 2 - Set
Note 2
ispwDownloadIncl: true ensures that any copybook that is referenced by any of the components will be downloaded alongside, even if they are not part of the assignment. This ensures that SonarQube gets all required files and does not flag false negative issues.
stage("Retrieve Code From ISPW")
{
checkout(
[
$class: 'IspwContainerConfiguration',
connectionId: "${HCI_Conn_ID}",
credentialsId: "${HCI_Token}",
componentType: '',
containerName: ISPW_Assignment,
containerType: '0',
ispwDownloadAll: false,
ispwDownloadIncl: true,
serverConfig: '',
serverLevel: ISPW_Target_Level
]
)
}
Stage # - Download Topaz for Total Test assets from GitHub
This stage use a Git clone to download the Topaz for for Total Test assets for the ISPW stream and application. The convention used in the example is that the name of the repository is made up from the stream name and application name, e.g. FTSDEMO_RXN3_Total_Tests. The code has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": Checkout, "SCM": Git.
Note
Using the relativeTargetDir parameter results in the content of the repository to be cloned into a dedicated sub folder of the Jenkins workspace. This simplifies execution of the test scenarios.
stage("Retrieve Tests")
{
Git_URL = "${Git_URL}/${Git_Ttt_Repo}"
checkout(
changelog: false,
poll: false,
scm: [
$class: 'GitSCM',
branches: [[
name: "*/${Git_Branch}"
]],
doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false,
extensions: [[
$class: 'RelativeTargetDirectory',
relativeTargetDir: "${TTT_Base_Folder}"
]],
submoduleCfg: [],
userRemoteConfigs: [[
credentialsId: "${Git_Credentials}",
name: 'origin',
url: "${Git_URL}"
]]
]
)
}
Execute test scenarios
Using the single Topaz for Total Test CLI, we can use a single call to the Topaz for Total Test plugin to execute all test scenarios for the desired environment (environmentId) and list of affected programs (jsonFile). The code for the latter has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": totaltest.
Note 1
The Git repository in use for these tutorials, contains Virtualized and Non Virtualized scenarios. Specifying this folder on the folderPath allows executing only test scenarios of a certain kind, in this case only Virtualized scenarios.
Note 2
contextVariables are used to set the correct load library at runtime.
stage("Execute related Unit Tests")
{
totaltest(
serverUrl: CES_Url,
serverCredentialsId: HCI_Token,
credentialsId: HCI_Token,
environmentId: TTT_Vt_Environment,
localConfig: false,
folderPath: TTT_Base_Folder + '/' + TTT_Vt_Folder,
recursive: true,
selectProgramsOption: true,
jsonFile: ISPW_Changed_Programs_File,
haltPipelineOnFailure: false,
stopIfTestFailsOrThresholdReached: false,
createJUnitReport: true,
createReport: true,
createResult: true,
createSonarReport: true,
contextVariables: '"ispw_app=' + ISPW_Application + ',ispw_level=' + ISPW_Target_Level + '"',
collectCodeCoverage: true,
collectCCRepository: CC_Repository,
collectCCSystem: ISPW_Application,
collectCCTestID: BUILD_NUMBER,
clearCodeCoverage: false,
logLevel: 'INFO'
)
After execution of the test scenarios, the results are being passed to the JUnit plugin. This will generate a diagram showing development of the test results over time. Also, it allows you to drill into the test results to determine which test cases and assertions failed.
junit(
allowEmptyResults: true,
keepLongStdio: true,
testResults: "TTTUnit/*.xml"
)
}
Stage # - Download Code Coverage results after test execution
This stage will download the code coverage results stored in the Xpediter Code Coverage repository on the mainframe to the Jenkins workspace. The results will be placed in the Coverage subfolder.
During download the plugin matches the downloaded source for each program it finds coverage data for against the corresponding DDIO file. The listing in the DDIO file must be preprocessed when code coverage is to be shown in SonarQube. This way it makes sure that code coverage information ending up in SonarQube actually flags the right statements as not being executed or being executed. Therefore the parameter cc.sources is required to point to the folder containing the downloaded sources.
The properties defined by the cc. parameters need to be one parameter per line, therefore \r is being used.
The code for downloading the code coverage results has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": step, "Build step": Retrieve Xpediter Code Coverage Statistics.
stage("Collect Coverage Metrics")
{
def ccSources = "${ISPW_Application}/${MF_Source}"
def ccProperties = 'cc.sources=' + ccSources +
'\rcc.repos=' + CC_Repository +
'\rcc.system=' + ISPW_Application +
'\rcc.test=' + BUILD_NUMBER +
'\rcc.ddio.overrides=' + CC_DDIO_Override
step(
[
$class: 'CodeCoverageBuilder',
connectionId: HCI_Conn_ID,
credentialsId: HCI_Token,
analysisProperties: ccProperties
]
)
}
Stage # - Pass data to SonarQube using SonarScanner
This stage will pass the downloaded COBOL sources, the results of the unit tests, and code coverage metrics to SonarQube using the Sonar Scanner.
The tool method returns the installation path of to the SonarScanner. withSonarQubeEnv retrieves information about the SonarQube server, which then does not need to be specified via parameters for the SonarScanner. Since the Topaz for Total Test plugin creates one result file per test scenario, the location and name of all of these files need to be passed to the SonarScanner via the sonar.testExecutionReportPaths parameter. The value will have to be a comma separated list of path and file names which is built in the initial stage.
stage("Check SonarQube Quality Gate")
{
def scannerHome = tool SQ_Scanner_Name
withSonarQubeEnv(SQ_Server_Name)
{
bat "${scannerHome}/bin/sonar-scanner " +
" -Dsonar.tests=${TTT_Base_Folder}" +
" -Dsonar.testExecutionReportPaths=${TTT_Sonar_Results_File}" +
" -Dsonar.coverageReportPaths=Coverage/CodeCoverage.xml" +
" -Dsonar.projectKey=${JOB_NAME}" +
" -Dsonar.projectName=${JOB_NAME}" +
" -Dsonar.projectVersion=1.0" +
" -Dsonar.sources=${ISPW_Application}/${MF_Source}" +
" -Dsonar.cobol.copy.directories=${ISPW_Application}/${MF_Source}" +
" -Dsonar.cobol.file.suffixes=cbl,testsuite,testscenario,stub,result,scenario" +
" -Dsonar.cobol.copy.suffixes=cpy" +
" -Dsonar.sourceEncoding=UTF-8"
}
After the results have been passed to SonarQube, query the resulting Sonar quality gate, by registering a Sonar Webhook call back. timeout will wait up to the specified time for the results of the quality gate to be returned.
timeout(time: 2, unit: 'MINUTES') {
def qg = waitForQualityGate()
The results can be queried by the status property. If the status is not okay, i.e. the quality gate failed, the assignments corresponding to the set will be regressed using the ISPW operation plugin (opens new window), an email is sent to the owner of the set, and the pipeline being aborted using the error method.
The code to regress the assignment has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": ispwOperation.
Note
The currentBuild.result = "FAILURE" sets the result of the pipeline to "FAILURE" without interrupting execution. This allows the emailext to pick up the correct status when sending an email.
Only after sending the mail do we abort the pipeline, using error.
if (qg.status != 'OK')
{
echo "Sonar quality gate failure: ${qg.status}"
echo "Pipeline will be aborted and ISPW Assignment will be regressed"
echo "Regress Assignment ${ISPW_Assignment}, Level ${ISPW_Target_Level}"
ispwOperation(
connectionId: HCI_Conn_ID,
credentialsId: Jenkins_CES_Token,
consoleLogResponseBody: true,
ispwAction: 'RegressAssignment',
ispwRequestBody: """
runtimeConfiguration=${ISPW_Runtime}
assignmentId=${ISPW_Assignment}
level=${ISPW_Target_Level}
"""
)
currentBuild.result = "FAILURE"
emailext(
subject: '$DEFAULT_SUBJECT',
body: '$DEFAULT_CONTENT',
replyTo: '$DEFAULT_REPLYTO',
to: "${mailRecipient}"
)
error "Exiting Pipeline"
}
}
}
Stage # - Trigger XLRelease release
If the quality gate passes, i.e. the pipeline does not get aborted, an XL Release template will be triggered - using the XL Release plugin - to execute CD stages beyond the Jenkins pipeline. The code has been generated by the Jenkins Syntax Generator using "Sample step": xlrCreateRelease.
Note
The propertyName, propertyValue pairs reflect the parameters that are required by the XL Release template.
stage("Start release in XL Release")
{
xlrCreateRelease(
releaseTitle: 'A Release for $BUILD_TAG',
serverCredentials: "${XLR_User}",
startRelease: true,
template: "${XLR_Template}",
variables: [
[propertyName: 'ISPW_Dev_level', propertyValue: "${ISPW_Target_Level}"],
[propertyName: 'ISPW_RELEASE_ID', propertyValue: "${ISPW_Release}"],
[propertyName: 'CES_Token', propertyValue: "${CES_Token}"]
]
)
}
}
